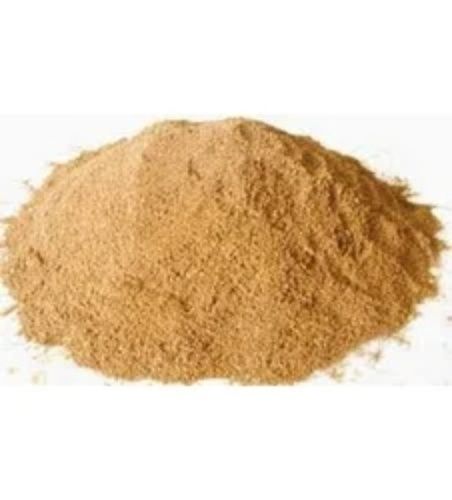
Tocopherol (Vitamine E)
1650 INR/Kilograms
Product Details:
- Product Type Herbal Product
- Category Herbs & Herbs Extract
- Usage HERBAL and health
- Ingredients Herbal Extract
- Form Oil
- Grade Herbal
- Recommended For All
- Click to View more
X
Tocopherol (Vitamine E) Price And Quantity
- 1650 INR/Kilograms
- 100 Kilograms
Tocopherol (Vitamine E) Product Specifications
- Herbal Extract
- at room temperature
- Herbal
- 2 Years
- HERBAL and health
- All
- Herbal Product
- Herbs & Herbs Extract
- Oil
Tocopherol (Vitamine E) Trade Information
- Cash in Advance (CID)
- 1000 Kilograms Per Week
- 2 Week
- All India
Product Description
that is essential for the maintenance of healthy skin. Naturally occurring vitamin E is not a single compound; instead, vitamin E is a group of molecules with related structures, some of which may have unique properties in skin. Vitamin E is also found as vitamin E conjugates that increase stability but require cellular metabolism for activation. Vitamin E is normally provided to the skin through the sebum. Topical application can also supply the skin with vitamin E and may provide specific vitamin E forms that are not available from the diet. As an antioxidant, vitamin E primarily reacts with reactive oxygen species. In addition, vitamin E can also absorb the energy from ultraviolet (UV) light. Thus, it plays important roles in photoprotection, preventing UV-induced free radical damage to skin. Vitamin E may also have related anti-inflammatory roles in the skin. Other roles of vitamin E in the skin are poorly understood because research is limited. This article discusses the roles of vitamin E in the skin and summarizes the current knowledge about vitamin E in skin health.Tell us about your requirement

Price:
Quantity
Select Unit
- 50
- 100
- 200
- 250
- 500
- 1000+
Additional detail
Mobile number
Email








 Send Inquiry
Send Inquiry Send SMS
Send SMS Call Me Free
Call Me Free English
English Spanish
Spanish French
French German
German Italian
Italian Chinese (Simplified)
Chinese (Simplified) Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Arabic
Arabic Portuguese
Portuguese